Table of Contents
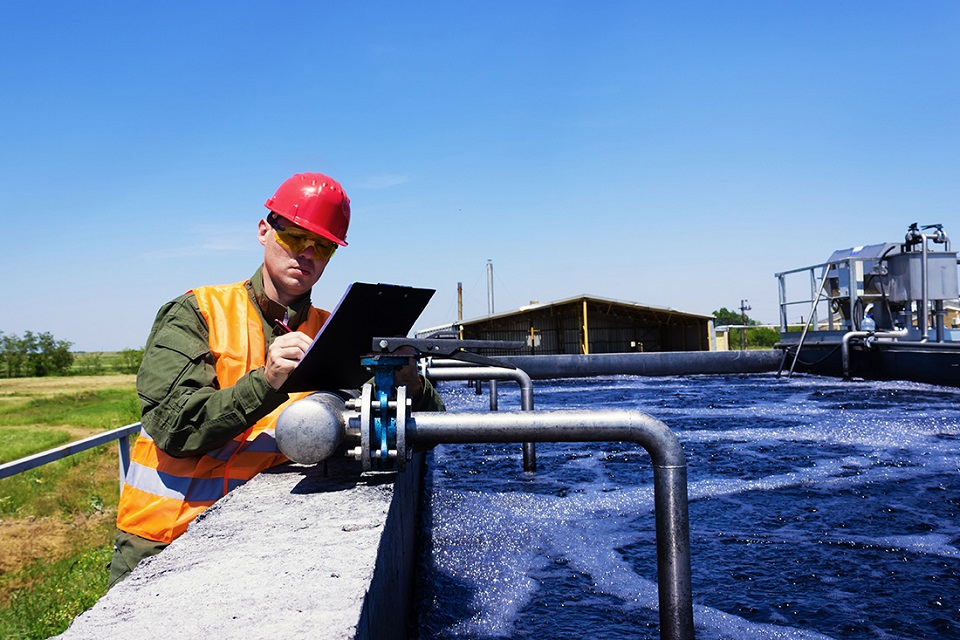
A wastewater treatment service filters solids from liquid. This waste is generated through industrial processes and human activities. The environment can only handle so much pollution, so wastewater treatment plants reduce the number of pollutants that enter the water supply. Clean water is vital for all life, human recreation, and health. If you are looking for a water treatment service, there are a few things to consider. Let’s explore each of them in more detail.
Disinfection
Depending on the chemical agent used, raw water may contain various contaminants that interfere with the disinfection process or may be unwanted in the finished product. Among these are organic and inorganic molecules, particulates, and organisms. Depending on regional geochemistry and differences between ground and surface-water sources, different contaminants exert different “demands” on disinfectants. Higher “demand” waters require a higher dose than lower “demand” waters. Consequently, the concentrations of disinfectants must be adjusted to achieve adequate biocidal treatment.
Two main types of disinfectants are used to treat water. One disinfectant uses chemical agents, while the other is based on physical agents. Chemical agents remove organic contaminants that provide nourishment and shelter for microorganisms. Besides killing the organisms, they must also produce a residual effect. The residual effect is essential in water treatment because pathogenic microorganisms can continue to grow and multiply in plumbing even after disinfection.
Filtration
Filtration is a process used to remove impurities from surface water and wastewater. The process improves water quality, taste, and appearance. In addition, filtration helps users meet strict permit requirements. It uses a variety of technologies to remove solids. Filtration is often used in industrial settings, where water is used in boilers, cooling make-up, and food and pharmaceutical manufacturing. It is also used to treat wastewater from sewerage treatment facilities.
The primary purpose of filtration is to remove suspended solids from water. Different mechanisms occur during filtration, including flocculation, sedimentation, and surface capture. Depending on the contaminant, filtration methods can be classified by the leading agencies involved. Surface capture consists of excluding particles from the water surface; in-depth filtration involves the deposition of solids within the filter media.
Chlorination
Chlorination is a method for disinfecting water. The chemical chlorine is dissolved in water and forms radicals that kill pathogens. These ions attack the cell membranes of bacteria and other microorganisms. Chlorine is a disinfectant because it can destroy many bacteria, viruses, organic matter, and color. Chlorination takes about thirty minutes to kill harmful bacteria and viruses and remove dissolved solids from water.
The chlorine demand depends on the quality of untreated water. Chlorine is a weak disinfectant, so it quickly combines with other elements in the water. In addition to ammonia and organic color, chlorine can be combined with microorganisms. However, a more efficient form of chlorine is available to treat water. There are two formulations of chlorine: solid and liquid. The former has fewer side effects but is more expensive.
Sedimentation
Generally, the most straightforward method of sedimentation is horizontal flow tanks. The water flowing through a horizontal flow tank contains suspended particles and settles on the bottom as it flows. The goal of this method is to separate the majority of suspended particles before they reach the overflow weirs. Horizontal flow tanks typically have sloped floors to collect sediment and discharge it to a discharge point. The process can also be carried out using chemicals and other methods.
The sedimentation process is essential because it reduces the concentration of particles in water, which minimizes the need for flocculation and coagulation. Sedimentation can also enhance the effectiveness of continuous filtration. Sedimentation is also done based on particle concentration. Smaller particles can settle without assistance, while larger particles require additional support. Once the sedimentation process is completed, it may be followed by a filtration process, including osmosis.
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis water treatment is a relatively low-maintenance process. You can do the maintenance yourself by changing the filters and membranes regularly. You should replace the pre-filters every two to three years. To keep your system running optimally, you should change them more frequently. A high-quality system should last about five years. If you don’t change the pre-filters, your system can malfunction and need replacement, which is costly.
The best option for a residential reverse osmosis system is a point-of-use unit. These are typically installed under a sink. Whole-house reverse osmosis systems require a large storage tank and a booster pump to maintain sufficient water pressure. The reverse-osmosis system has three different types of cartridges and filters. All three types have their advantages and disadvantages. The best one is cost-effective, eliminating the need to buy bottled water. It also removes 99% contaminants, making it an excellent choice for commercial applications.




No Comments